Originates from surface of the iliac fossa and anterior inferior iliac spine. Its fibres combine with the tendon of the psoas major inserting into the lesser trochanter of the femur.

Figure Anatomy Of The Brain The Pdq Cancer Information Summaries Ncbi Bookshelf
Three cases are presented with a previously unreported otologic symptom that of bilateral hearing loss which in one case was fluctuant.
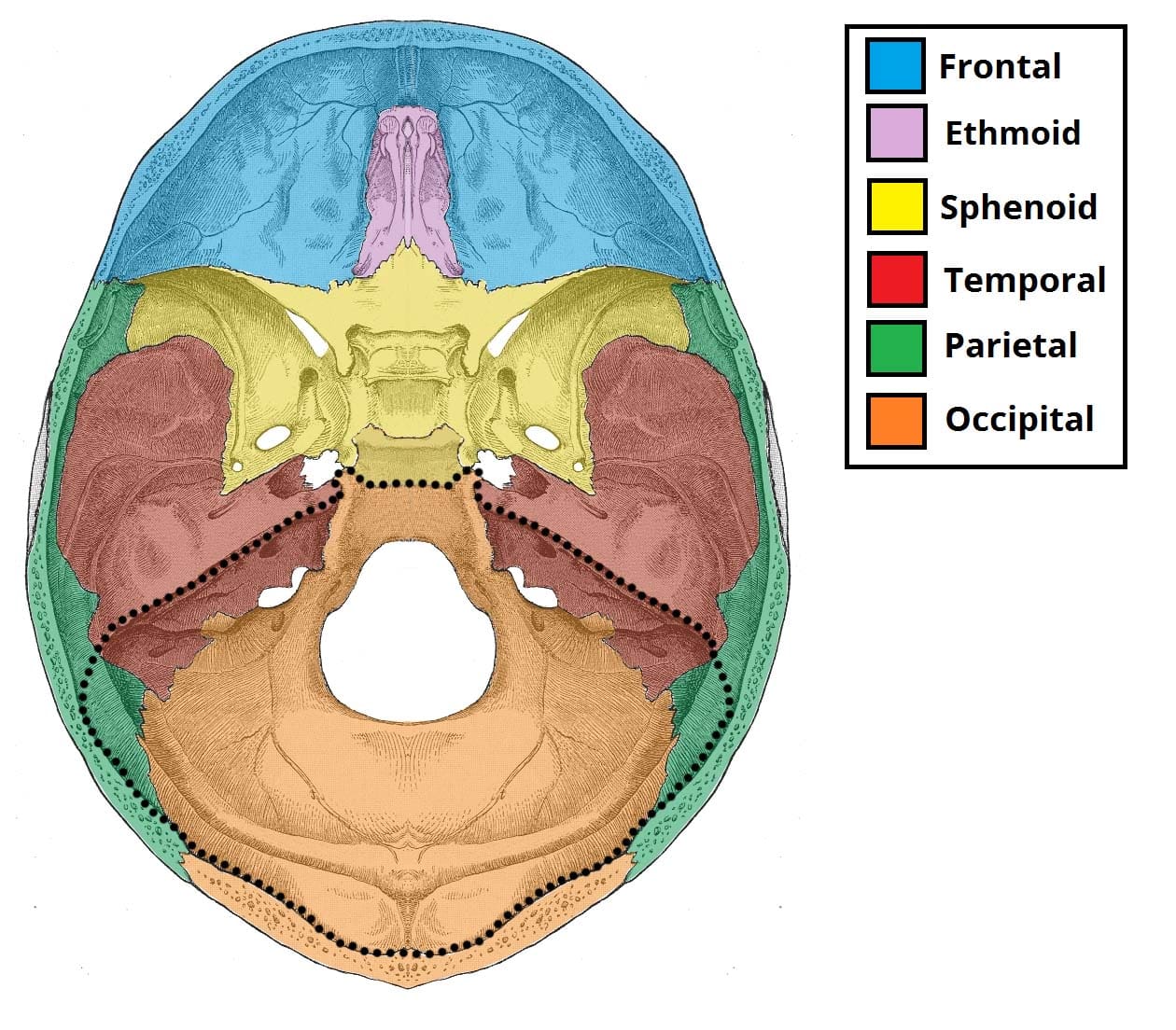
. Cerebellar metastases most common especially lung cancer and breast cancer. The posterior fossa is a small space in the skull found near the brainstem and cerebellum. It is said to be butterfly shaped with a middle part accommodating the pituitary gland and two lateral parts accommodating the.
Arachnoid cysts of the posterior fossa are rare. None of the patients had the common. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for balance and coordinated movements.
Posterior may refer to. Also melanoma thyroid malignancies and renal cell cancer. Foundations of Medicine II.
The posterior aspect of the diaphragm is considered to be part of. Most common posterior fossa primary brain tumor in adults. During fetal development the foramen ovale allows blood to pass from the right atrium to the left atrium.
The posterior fossa is a small space in the skull found near the brainstem and cerebellum. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor very rare 5. Amygdaloid fossa the depression in which the tonsil is lodged.
First Year Medical Anatomy. Posterior tense a relative future tense This page was last edited on 11 November 2020 at 1517 UTC. Posterior fossa tumor has a very different differential in an adult as opposed to a child.
Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain. Fossae L a trench or channel. The fossa ovalis is a depression in the right atrium of the heart at the level of the interatrial septum the wall between right and left atrium.
Anatomy Faculty and Staff - M1. The fossa ovalis is the remnant of a thin fibrous sheet that covered the foramen ovale during fetal development. Flexion and lateral rotation of the thigh at the hip joint.
Posterior anatomy the end of an organism opposite to its head Buttocks as a euphemism. Posterior horn disambiguation Posterior probability the conditional probability that is assigned when the relevant evidence is taken into account. Coronoid fossa a depression in the humerus for the.
The middle cranial fossa is located as its name suggests centrally in the cranial floor. Condylar fossa condyloid fossa either of two pits on the lateral portion of the occipital bone. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa.
The brainstem is responsible for controlling vital body functions such as breathing. In anatomy a hollow or depressed area. If a tumor grows in the area of the posterior fossa it can block the flow of spinal fluid and.
Femoral nerve L2 L4. Cerebral fossa any of the depressions on the floor of the cranial cavity. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for balance and coordinated movements.
When arachnoid cysts are encountered the presenting symptoms are frequently otologic with hearing loss and imbalance occurring commonly. The brainstem is responsible for controlling vital body functions such as breathing.

Posterior Cranial Fossa Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy

Posterior Cranial Fossa Wikipedia

Posterior Cranial Fossa Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Posterior Cranial Fossa Wikipedia

Anatomical Location Of Posterior Fossa Meningiomas Cerebellar Download Scientific Diagram
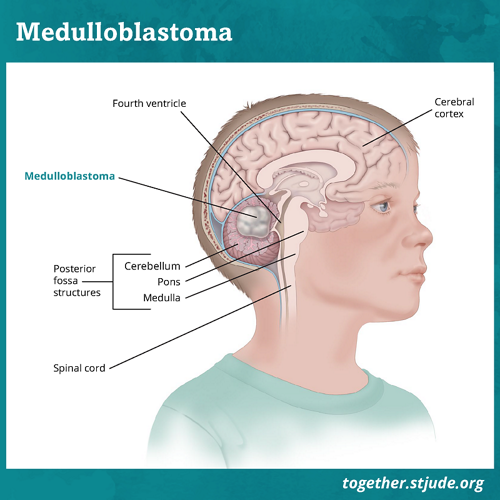
Posterior Fossa Syndrome Together
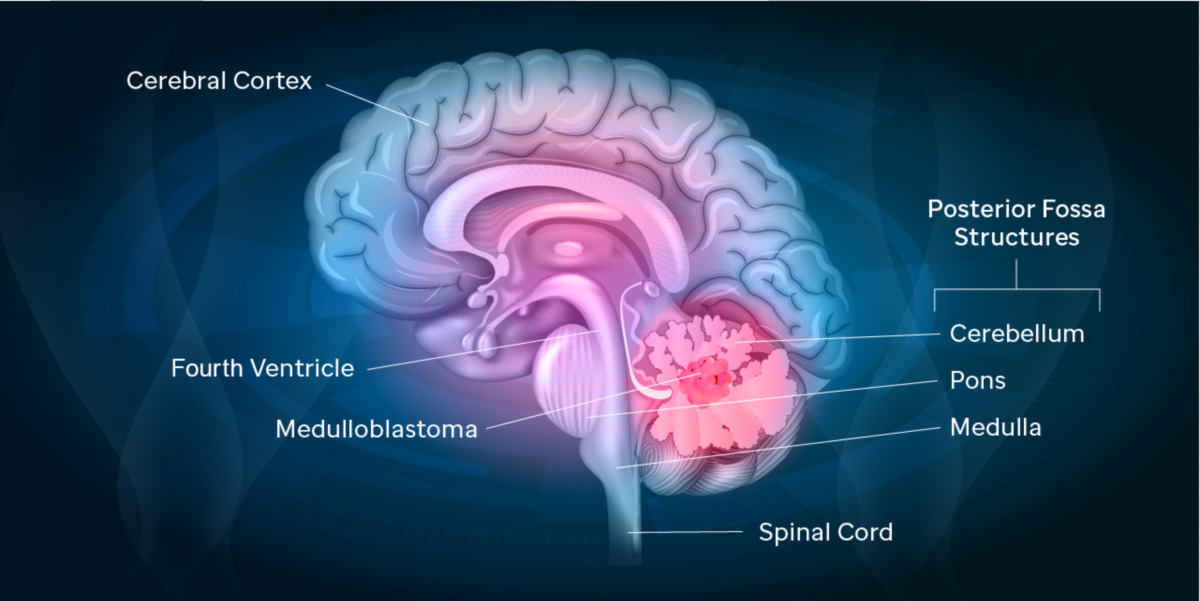
Getting To The Bottom Of A Medulloblastoma Mystery St Jude Progress
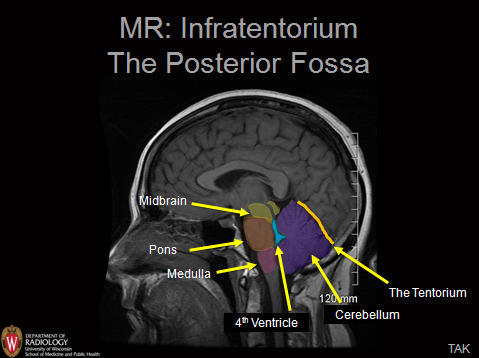
0 comments
Post a Comment